Exploring Ancient Wonders: From Mummies to Lost Civilizations

When the word “mummy” is mentioned, many instantly think of eerie, wrapped bodies from horror movies. However, real mummies have provided invaluable insights into ancient civilizations, their rulers, and their methods of coping with loss and the afterlife. These discoveries not only open a window to the past but also offer a glimpse into the spiritual and cultural beliefs that shaped the ancient world.
Ancient Egypt: The Birthplace of Mummification
Ancient Egypt is perhaps most renowned for its practice of mummification, a process that preserved bodies for the afterlife. The Egyptians believed that after death, the soul could continue its journey if the body was properly preserved. This belief was deeply connected to their understanding of nature—just as the sun rose every day and new plants grew after withering, they saw death and resurrection as part of the natural cycle.
One of the most famous mummies is that of King Tutankhamun, the young pharaoh whose tomb was discovered in 1922. Unlike many other royal tombs, King Tut’s burial site had not been plundered by tomb robbers, providing a wealth of artifacts and a preserved mummy. This discovery allowed researchers to learn about the ancient Egyptian practices and even study King Tut’s DNA, revealing that he had suffered from malaria and physical ailments that affected his mobility. Similarly, other mummies, such as Ramses II, have provided insight into the lives of Egypt’s rulers. Ramses II, for example, is believed to have had a medical condition that affected his spine, a detail discovered from studying his mummified remains.
The Mummification Process: An Art and Science
The mummification process in ancient Egypt could take up to 70 days. It involved a series of meticulous steps to preserve the body, such as removing the organs, drying the body with natron (a type of salt), and wrapping it in linen. The body would be treated with oils and resins to maintain its form, ensuring it would appear lifelike for the afterlife. Tombs were just as important as the mummification process itself, as they were seen as a person’s final residence in the afterlife. Pharaohs and important individuals were buried with goods, food, and even miniature versions of daily items, including clothing, jewelry, and games.
King Tut’s tomb, for example, contained 36 jars of vintage beverages and baskets of fruit, believed to sustain him in his journey to the afterlife. The tomb’s walls were adorned with intricate artwork, depicting his journey through the underworld, as well as spells to guide him.
Ancient South America: The First Mummification Culture
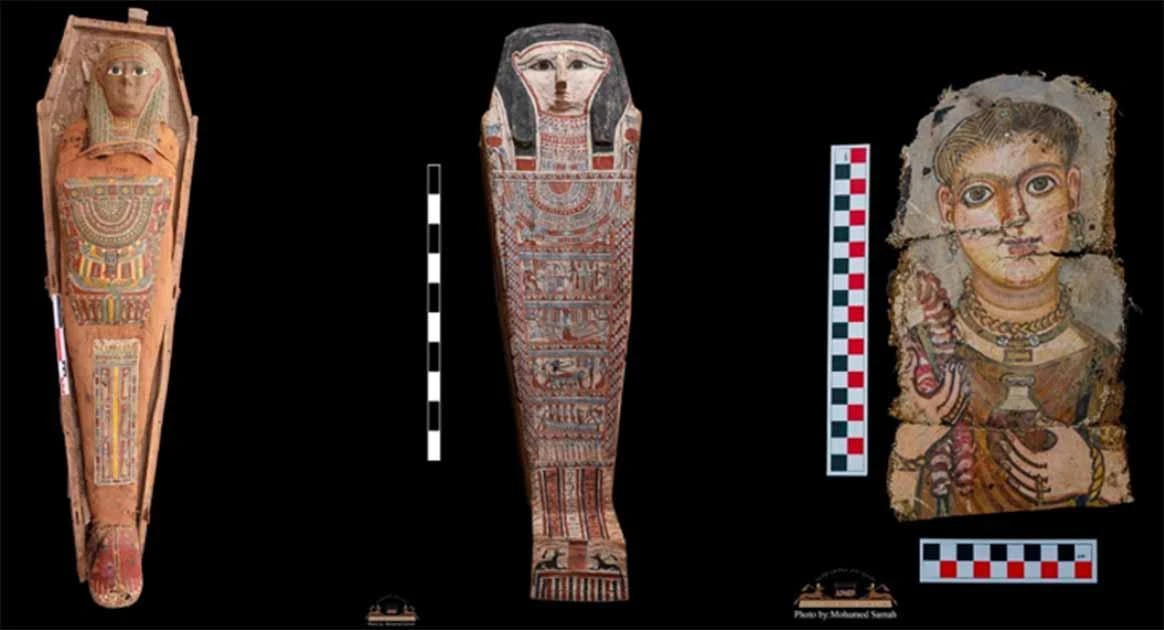
While Egypt’s mummies are the most famous, they weren’t the first civilization to practice mummification. Long before the Egyptians, the Chinchorro people in South America were the pioneers of mummification. This culture, located in modern-day Chile and Peru, began the practice approximately 2,000 years before the Egyptians. The Chinchorro mummies are notable for being some of the oldest known mummies in the world.
Mummy Portraits: A Glimpse of Life Before Death
Mummification has often left us with skeletal remains, but recent discoveries have introduced a fascinating new element to understanding ancient lives—mummy portraits. These detailed paintings were often placed over the face of the deceased, offering a lifelike representation of the individual as they appeared when alive. Discovered in central Egypt, these mummy portraits have provided rare insights into the clothing, jewelry, and even the health of the deceased. They represent the human side of these ancient cultures, revealing personal details that mummified remains alone could not convey.
The Mayan Civilization: Astronomical Builders of the Past
While the Egyptians were busy perfecting the art of mummification, the Mayan civilization in Central America was creating its own set of monumental wonders. The Mayans were not only great architects and mathematicians but also keen astronomers. They mapped the stars and predicted eclipses with remarkable accuracy. Their knowledge of astronomy extended into their city planning, as many Mayan cities were aligned with celestial bodies.
One particularly intriguing discovery came from a young Canadian teenager, William Gadie, who used satellite imagery to uncover a potential lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula. Gadie noticed that the ancient Mayan cities aligned with the stars, and he discovered a previously unknown location that could hold the remains of a third city that had been lost to history.
The Mayans were known for their complex pyramids, ceremonial ball courts, and intricate urban planning. Their cities, such as Chichen Itza and Uxmal, were once thriving centers of culture and trade, and these new discoveries continue to paint a picture of the Mayan civilization’s greatness.
Mummification and Natural Preservation
Not all mummies were created through deliberate human action. Some were preserved through natural conditions, like extreme heat, cold, or lack of oxygen. A famous example is Ötzi the Iceman, discovered in the Alps in 1991. This mummy, dating back over 5,000 years, was so well-preserved that it took scientists by surprise. Initially mistaken for a modern mountaineer, Ötzi was later determined to be from the Copper Age, offering a fascinating glimpse into prehistory.
The Sphinx and Other Monumental Discoveries
Monumental discoveries, like the Great Sphinx in Egypt, also offer a glimpse into the ancient world. For centuries, the Sphinx’s head was buried in sand until it was unearthed in the early 19th century. The Sphinx, along with the pyramids of Giza, is one of the most iconic symbols of ancient Egypt, and it continues to fascinate archaeologists and tourists alike.
Meanwhile, archaeological projects around the world continue to unearth ancient cities and artifacts that shed light on the lost civilizations of the past. Recent findings in the Talamakan Desert in China and the Middle East continue to push the boundaries of our knowledge, revealing how ancient peoples lived and adapted to their environments.
Unearthing the Past: The Role of Modern Technology

Today, archaeologists have tools at their disposal that were unimaginable in the past. Advanced technologies, such as satellite imagery and ground-penetrating radar, allow researchers to explore the earth in new ways. These tools have been instrumental in discovering ancient cities and monuments that would otherwise remain hidden beneath layers of soil and vegetation.
For example, Brazilian researchers used satellite imagery to uncover a network of ancient trenches and settlements that may have supported up to 60,000 people. Similar technology is now being used to explore the lost Mayan cities and ancient Egyptian structures, providing new insights into these civilizations’ infrastructure, social structure, and daily life.
Conclusion: A Window to the Past
The discoveries of mummies, ancient cities, and artifacts from around the world continue to reshape our understanding of history. From the tombs of Egypt to the lost Mayan cities, each new find reveals more about the complex societies that existed long before us. As technology continues to advance, who knows what other secrets of the past remain to be uncovered, waiting to rewrite history once again.
In a world where the past and present constantly collide, each discovery adds another layer to the rich tapestry of human civilization. The more we uncover, the more we realize just how much we still have to learn about the people who came before us.
News
The Surgeon Stared in Horror as the Patient Flatlined—Until the Janitor Stepped Forward, Eyes Cold, and Spoke Five Words That Shattered Protocol, Saved a Life, and Left Doctors in Shock
“The Janitor Who Saved a Life: A Secret Surgeon’s Quiet Redemption” At St. Mary’s Hospital, the night shift is often…
Tied Up, Tortured, and Left to Die Alone in the Scorching Wilderness—She Gasped Her Last Plea for Help, and a Police Dog Heard It From Miles Away, Triggering a Race Against Death
“The Desert Didn’t Take Her—A K-9, a Cop, and a Second Chance” In the heart of the Sonoran desert, where…
“She Followed the Barking Puppy for Miles—When the Trees Opened, Her Heart Broke at What She Saw Lying in the Leaves” What began as a routine patrol ended with one of the most emotional rescues the department had ever witnessed.
“She Thought He Was Just Lost — Until the Puppy Led Her to a Scene That Broke Her” The first…
“Bloodied K9 Dog Crashes Into ER Carrying Unconscious Girl — What He Did After Dropping Her at the Nurses’ Feet Left Doctors in Total Silence” An act of bravery beyond training… or something deeper?
The Dog Who Stopped Time: How a Shepherd Became a Hero and Saved a Little Girl Imagine a hospital emergency…
Rihanna Stuns the World with Haunting Ozzy Osbourne Tribute — A Gothic Ballad So Powerful It Reportedly Made Sharon Osbourne Collapse in Tears and Sent Fans into Emotional Meltdown at Midnight Release
“Still Too Wild to Die”: Rihanna’s Soul-Shattering Tribute to Ozzy Osbourne Stuns the Music World Lights fade slow, but your…
“Ignored for Decades, This Humble Waiter Got the Shock of His Life When a Rolls-Royce Arrived with a Note That Read: ‘We Never Forgot You’” A simple act of kindness returned as a life-altering reward.
A Bowl of Soup in the Snow: The Forgotten Act That Changed Two Lives Forever The town had never known…
End of content
No more pages to load












